Social Determinants of Health
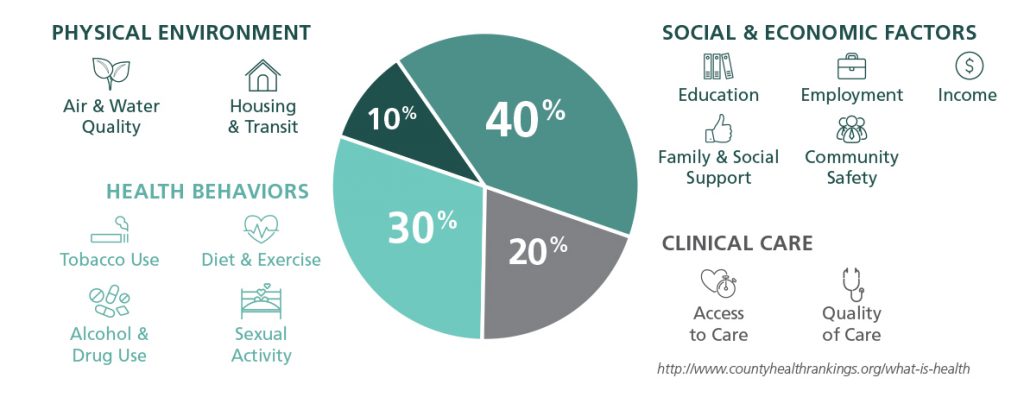
Health and wellbeing are foundational to economic vitality and business competitiveness, personal achievement, and prosperity. An increased level of health for all Americans is key to the promotion of thriving lives, economies, and communities. We support the Healthy People 2020 definition of the social determinants of health as the “conditions in the environments in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.” Health outcomes strongly relate to these upstream social determinants of health: non-medical factors such as food access and nutrition, transportation, housing, incarceration and recidivism, jobs/wages, safety, education, and other community-based and environmental conditions.
America's future rests on healthy people and healthy communities
The ability to lead healthy, productive lives is influenced by personal choices, but also by our experiences and the conditions in our communities. Improving health will require more than the best performing medical system. Bold public-private sector collaboration is needed to find more innovative and effective ways to improve health and curb health care spending, including investing in the social determinants of health.

To improve well-being and economic vitality, we must invest in the social determinants of health


To download this page and for more information, please click below:

![]()
Health and wellbeing are foundational to economic vitality and business competitiveness, personal achievement, and prosperity. An increased level of health for all Americans is key to the promotion of thriving lives, economies, and communities. We support the Healthy People 2020 definition of the social determinants of health as the “conditions in the environments in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.” Health outcomes strongly relate to these upstream social determinants of health: non-medical factors such as food access and nutrition, transportation, housing, incarceration and recidivism, jobs/wages, safety, education, and other community-based and environmental conditions.